UX Benchmarking Initiative
Defining UX Standards for a Genomic Workflow Platform
Avenio Connect is Roche’s workflow management platform for genomic sequencing labs. Lab technicians use the platform to track biological samples across a multi-stage sequencing pipeline - where missed steps, incorrect configuration, or workflow ambiguity can compromise downstream analysis and delay time-sensitive clinical decision-making.
Introducing Design Validation
While Avenio Connect enabled end-to-end sequencing workflow management, many critical tasks were not clearly guided within the interface. Technicians were often required to rely on prior training or external SOPs to configure sequencing runs — increasing onboarding time, support dependency, and the risk of incorrect or incomplete setup.
Recognizing the absence of a usability maturity baseline for sequencing workflows, I recommended conducting a benchmark usability study to evaluate how effectively the platform enabled technicians to independently complete key sequencing tasks.
The study was designed to identify points of workflow breakdown and establish a UX quality baseline to guide future workflow design decisions.
Design goals
Establish a usability baseline for Avenio Connect’s sequencing workflows to better understand how effectively the platform supports lab technicians in independently completing critical tasks - and identify opportunities to improve workflow guidance in future design iterations.
Business goals
Generate formative usability evidence required for FDA submission and IEC 62366-1 compliance to demonstrate that sequencing workflows can be completed safely and effectively within the platform.
A benchmark usability study provided a structured way to evaluate whether sequencing workflows could be completed safely within the platform while meeting regulatory requirements for usability validation.
Benchmarking Strategy
Study Objectives
The study was designed to evaluate how effectively Avenio Connect supported technicians in completing critical sequencing workflows without reliance on external documentation or prior training.
Key objectives included:
Assess whether technicians could independently complete key sequencing tasks within the platform
Identify points of workflow breakdown or task uncertainty
Evaluate how clearly the system communicated sequencing progress and system state
Understand where users relied on institutional SOPs or prior training to complete in-product tasks
Establish a usability baseline for future formative and summative evaluationsAssess whether technicians could independently complete key sequencing tasks within the platform
Metrics of Success
To determine whether sequencing workflows could be completed safely and effectively within the platform, the following success criteria were established:
Task completion rate for critical sequencing workflows
Time on task for configuration and setup steps
Frequency of user error during run configuration
Instances of workflow abandonment or task hesitation
Reliance on external documentation to complete in-product tasks
Participant confidence in sequencing setup decisions
These metrics provided a structured way to evaluate workflow support within the platform and establish a UX quality baseline for future design iterations.
Study Design
Test Setup
Design: Formative usability evaluation
Evaluation scope: End-to-end Avenio Connect flow
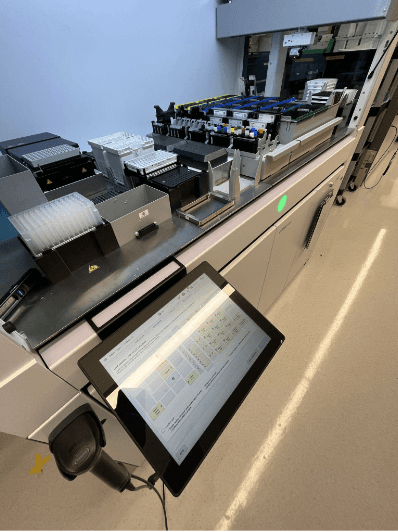
Materials: Avenio Connect software, Avenio Edge instrument, third party instruments
Location: Roche sequencing labs
Date: May 30 – June 29, 2023
Depending variables: use errors, usability issues, user quotations, system usability scale
Participants
Number of participants: 8
Gender: 5 female, 3 male
Working experience: Avg 10 years
Familiarity with Capstone IVD (Roche assay): 6 expert, 2 comfortable
Familiarity with Avenio Connect software: 1 expert, 6 comfortable, 1 novice
Work areas: 8 research and development
Participants were recruited from Roche’s research and development teams based on their familiarity with next-generation sequencing workflows. While most participants had extensive experience with Roche’s Capstone IVD assay (avg. 10 years working experience), the majority reported only moderate familiarity with Avenio Connect.
This allowed the study to evaluate how effectively the platform supported technicians who understood sequencing requirements but were not yet expert users of the software - a critical condition for assessing onboarding burden and reliance on in-product workflow guidance.
Lab Setup
Sequencing workflows are often completed in time-sensitive lab environments where technicians are responsible for managing multiple concurrent tasks. Evaluating Avenio Connect within this context was critical to understanding how environmental factors may influence task completion and configuration accuracy.
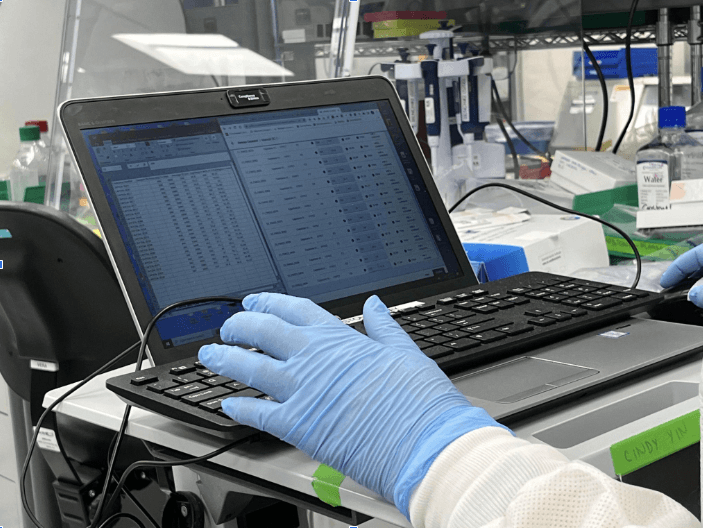
Participants were required to wear standard laboratory PPE, including lab coats, goggles, masks, gloves, and shoe covers. Several participants also used plastic laptop covers to avoid sanitizing their devices when exiting the lab.
Multiple workflow steps required technicians to pipette samples into wells or tubes while simultaneously using their laptops to calculate and enter data or reference instructions. These conditions introduced physical and attentional constraints that could impact how effectively users interacted with the platform while completing sequencing tasks.
Contextual Inquiry Session Breakdown
Because sequencing tasks in Avenio Connect are highly interdependent, evaluating individual interface interactions in isolation would not adequately capture points of workflow breakdown. An observational, task-based study was conducted to assess whether technicians could complete an end-to-end sequencing workflow within the platform.
Participants were asked to complete each workflow using only the guidance available within Avenio Connect. This allowed the team to evaluate how effectively the platform supported task completion without reliance on external SOPs or prior software training.
During the observational portion of each session, we focused on identifying:
task hesitation prior to sequencing configuration
reliance on prior knowledge to complete in-product tasks
misinterpretation of sequencing progress or system state
unconventional task completion that may introduce configuration risk
Post-session and SUS surveys were used to supplement observational findings by capturing participant confidence in completing each step of the sequencing process.
Each session lasted for 3-4 days and was recorded and annotated.
What We Learned
All notes taken throughout each session were hand-coded to turn qualitative data into quantitative data. Each session was transcribed and separated into issues, findings, and comments. Those entries were later given severity levels to help determine issue priority. Issues categorized as catastrophic revealed a misalignment between Avenio Connect’s enforced sequencing methodology and technicians’ existing workflow mental models.
The Primary Problem
Avenio Connect enforced a rigid sequencing methodology that required all samples to progress through workflow steps simultaneously. Participants perceived the platform’s safety constraints as excessively limiting, particularly when adapting to unforeseen lab conditions.
As a result, technicians were often required to make sequencing decisions prematurely in order to proceed through the workflow. This introduced risk of incorrect run configuration, potentially compromising sample data integrity or resulting in the loss of costly reagents.
Other findings

Physical Interaction Constraints
Technicians frequently interacted with Avenio Connect on small laptops while moving throughout the lab in PPE. These conditions introduced physical limitations that impacted how easily users could review sequencing instructions or enter configuration data during critical workflow steps.

OPERATIONAL FRICTION
Participants spent significant time manually entering sample data for sequencing runs, increasing administrative burden during active lab procedures and diverting attention from sequencing tasks.
Limited in-product workflow guidance
Participants often expressed uncertainty about how to proceed between sequencing steps when guidance was not available within the platform, increasing reliance on memory or external SOPs to continue task completion.

Limited Error Recovery During Configuration
Manual configuration inputs were difficult to edit once submitted, limiting technicians’ ability to recover from sequencing setup errors and increasing the likelihood of run invalidation or reagent loss.
Beyond informing immediate product improvements within Avenio Connect, the benchmark usability study also influenced how sequencing product teams at Roche approached workflow design and usability evaluation more broadly.
By establishing a structured baseline for how technicians interact with sequencing software in real laboratory environments, the study provided product and engineering stakeholders with a shared understanding of where current workflows aligned (or conflicted) with user expectations. This created new visibility into use-related risks that had previously been addressed through training or SOPs rather than in-product guidance.
As a result, UX research became more closely integrated into sequencing product development efforts across Roche, with multiple teams expressing interest in adopting similar formative evaluation methods to assess workflow support and configuration safety within their own platforms.
Established a model for UX Evaluation
The benchmark usability study generated interest across sequencing product teams at Roche, many of whom began adopting similar formative evaluation methods to assess workflow support within their own platforms.
Accelerated iterative design practices
Findings from the study resulted in 45 design tickets, creating urgency for product teams to incorporate usability findings earlier and more frequently throughout the development cycle.
Enabled data-informed workflow design
By establishing a usability baseline across each step of the NGS process, the study allowed product teams to make design decisions grounded in observed technician workflows - reducing reliance on internal assumptions about user behavior.